
A short video explaining the seasons and how nature changes within the year. Video also discusses how we change to adapt to the different seasons. [3:00]
- Subject:
- Science
- Material Type:
- Audio/Video
- Provider:
- PBS LearningMedia
- Date Added:
- 12/01/2022

A short video explaining the seasons and how nature changes within the year. Video also discusses how we change to adapt to the different seasons. [3:00]

Students explore Hooke's law while working in small groups at their lab benches. They collect displacement data for springs with unknown spring constants, k, by adding various masses of known weight. After exploring Hooke's law and answering a series of application questions, students apply their new understanding to explore a tissue of known surface area. Students then use the necessary relationships to depict a cancerous tumor amidst normal tissue by creating a graph in Microsoft Excel.
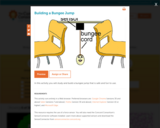
A bungee jump involves jumping from a tall structure while connected to a large elastic cord. Design a bungee jump that is "safe" for a hard-boiled egg. Create a safety egg harness and connect it to a rubber band, which is your the "bungee cord." Finally, attach your bungee cord to a force sensor to measures the forces that push or pull your egg.

Join PBS KIDS and explore the seasons: fall, winter, and spring! The lessons have been co-designed by museum and educational partners and feature many of your PBS KIDS friends. Introduce media clips, extension activities, articles, and crafts in your classroom and share resources with families to strengthen a school-to-home connection. Children will learn about the world around them through science, math, and art activities. As you engage in these lessons, you can feel confident that you are helping children grow up great! This Collection includes: Media Gallery (16), Video (16) for Grades PreK-K , Resources in Spanish (16).

This interactive resource adapted from the National Park Service describes the many forces that affect shorelines, including tides, weathering, erosion, and deposition. Includes background reading handout and discussion questions.

Read about the life cycle of dandelions from their first appearance in the spring. Includes audio narration in 16 additional languages with text in English.
Students disassemble and analyze retractable pens. Through the process of "reverse engineering," they learn how the ink pens work.
Students learn about weight by building a spring scale and observing how it responds to objects with different masses.

When spring arrives, there are lots of things for children to do. Includes audio narration in English, Spanish, and Turkish with text in English.
Students investigate potential energy held within springs (elastic potential energy) as part of the Research and Revise step. Class begins with a video of spring shoes or bungee jumping. Then students move on into notes and problems as a group. A few questions are given as homework. The Test Your Mettle section concludes. The lesson includes a dry lab that involves pogo sticks to solidify the concepts of spring potential energy, kinetic energy and gravitational energy, as well as conservation of energy.

A great resource for explaining and understanding tides. Find out what tides are and why it is so important to monitor them. This is an extensive tutorial followed by a set of review questions. All of the information can be downloaded as a 36-page PDF file.
Students learn about frequency and period, particularly natural frequency using springs. They learn that the natural frequency of a system depends on two things: the stiffness and mass of the system. Students see how the natural frequency of a structure plays a big role in the building surviving an earthquake or high winds.

This site from Georgia State University Physics Department defines and explains the concept of potential energy. Using equations and graphics to illustrate the idea, it discusses the many types of potential energy (gravitational, magnetic, electric, elastic, etc.) and gives examples of each. Links to further information on each type of potential energy are provided.
This lesson culminates the unit with the Go Public phase of the legacy cycle. In the associated activity, students depict a tumor amidst healthy body tissue using a Microsoft Excel® graph. In addition, students design a brochure for both patients and doctors advertising a new form of painless yet reliable breast cancer detection. Together, the in-class activity and the take-home assignment function as an assessment of what students have learned throughout the unit.
Students use data acquisition equipment to learn about force and displacement in regard to simple and complex machines. In the engineering world, materials and systems are tested by applying forces and measuring the resulting displacements. The relationship between the force applied on a material, and its resulting displacement, is a distinct property of the material, which is measured in order to evaluate the material for correct use in structures and machines.

Learn more about the four seasons and the weather that goes along with them. For ages 3-5.

This pathway explores the concept of simple harmonic motion. The pendulum and spring are used as foundational examples that are used to develop more complex models. Advanced application such as resonsnce are discussed
Students learn why shock absorbers are necessary on vehicles, how they dampen the action of springs, and what factors determine the amount of dampening. They conduct an experiment to determine the effect of spring strength and port diameter on the effectiveness of a shock absorber. Using a syringe, a set of springs, and liquids of different viscosities, students determine the effects of changing pressures and liquids on the action of a model shock absorber. They analyze their data through the lens of an engineer.
This lab demonstrates Hooke's Law with the use of springs and masses. Students attempt to determine the proportionality constant, or k-value, for a spring. They do this by calculating the change in length of the spring as different masses are added to it. The concept of a spring's elastic limit is also introduced, and the students test to makes sure the spring's elastic limit has not been reached during their lab tests. After compiling their data, they attempt to find an average value of the spring's k-value by measuring the slopes between each of their data points. Then they apply what they've learned about springs to how engineers might use that knowledge in the design of a toy that enables kids to jump 2-3 feet in the air.

Learn about springtime in the desert and the plants and animals that live there. Book includes audio narration in 20 additional languages with text in English.