POLITICAL SOCIALIZATION
At the same time that our beliefs and attitudes are forming during childhood, we are also being socialized; that is, we are learning from many information sources about the society and community in which we live and how we are to behave in it. Political socialization is the process by which we are trained to understand and join a country’s political world, and, like most forms of socialization, it starts when we are very young. We may first become aware of politics by watching a parent or guardian vote, for instance, or by hearing presidents and candidates speak on television or the Internet, or seeing adults honor the American flag at an event (Figure). As socialization continues, we are introduced to basic political information in school. We recite the Pledge of Allegiance and learn about the Founding Fathers, the Constitution, the two major political parties, the three branches of government, and the economic system.

By the time we complete school, we have usually acquired the information necessary to form political views and be contributing members of the political system. A young man may realize he prefers the Democratic Party because it supports his views on social programs and education, whereas a young woman may decide she wants to vote for the Republican Party because its platform echoes her beliefs about economic growth and family values.
Accounting for the process of socialization is central to our understanding of public opinion, because the beliefs we acquire early in life are unlikely to change dramatically as we grow older.John Zaller. 1992. The Nature and Origins of Mass Opinion. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Our political ideology, made up of the attitudes and beliefs that help shape our opinions on political theory and policy, is rooted in who we are as individuals. Our ideology may change subtly as we grow older and are introduced to new circumstances or new information, but our underlying beliefs and attitudes are unlikely to change very much, unless we experience events that profoundly affect us. For example, family members of 9/11 victims became more Republican and more political following the terrorist attacks.Eitan Hersh. 2013. “Long-Term Effect of September 11 on the Political Behavior of Victims’ Families and Neighbors.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 110 (52): 20959–63. Similarly, young adults who attended political protest rallies in the 1960s and 1970s were more likely to participate in politics in general than their peers who had not protested.M. Kent Jennings. 2002. “Generation Units and the Student Protest Movement in the United States: An Intra- and Intergenerational Analysis.” Political Psychology 23 (2): 303–324.
If enough beliefs or attitudes are shattered by an event, such as an economic catastrophe or a threat to personal safety, ideology shifts may affect the way we vote. During the 1920s, the Republican Party controlled the House of Representatives and the Senate, sometimes by wide margins.United States Senate. 2015. “Party Division in the Senate, 1789-Present,” United States Senate. June 5, 2015. http://www.senate.gov/pagelayout/history/one_item_and_teasers/partydiv.htm (February 17, 2016). History, Art & Archives. 2015. “Party Divisions of the House of Representatives: 1789–Present.” United States House of Representatives. June 5, 2015. http://history.house.gov/Institution/Party-Divisions/Party-Divisions/ (February 17, 2016). After the stock market collapsed and the nation slid into the Great Depression, many citizens abandoned the Republican Party. In 1932, voters overwhelmingly chose Democratic candidates, for both the presidency and Congress. The Democratic Party gained registered members and the Republican Party lost them.V. O. Key Jr. 1955. “A Theory of Critical Elections.” Journal of Politics 17 (1): 3–18. Citizens’ beliefs had shifted enough to cause the control of Congress to change from one party to the other, and Democrats continued to hold Congress for several decades. Another sea change occurred in Congress in the 1994 elections when the Republican Party took control of both the House and the Senate for the first time in over forty years.
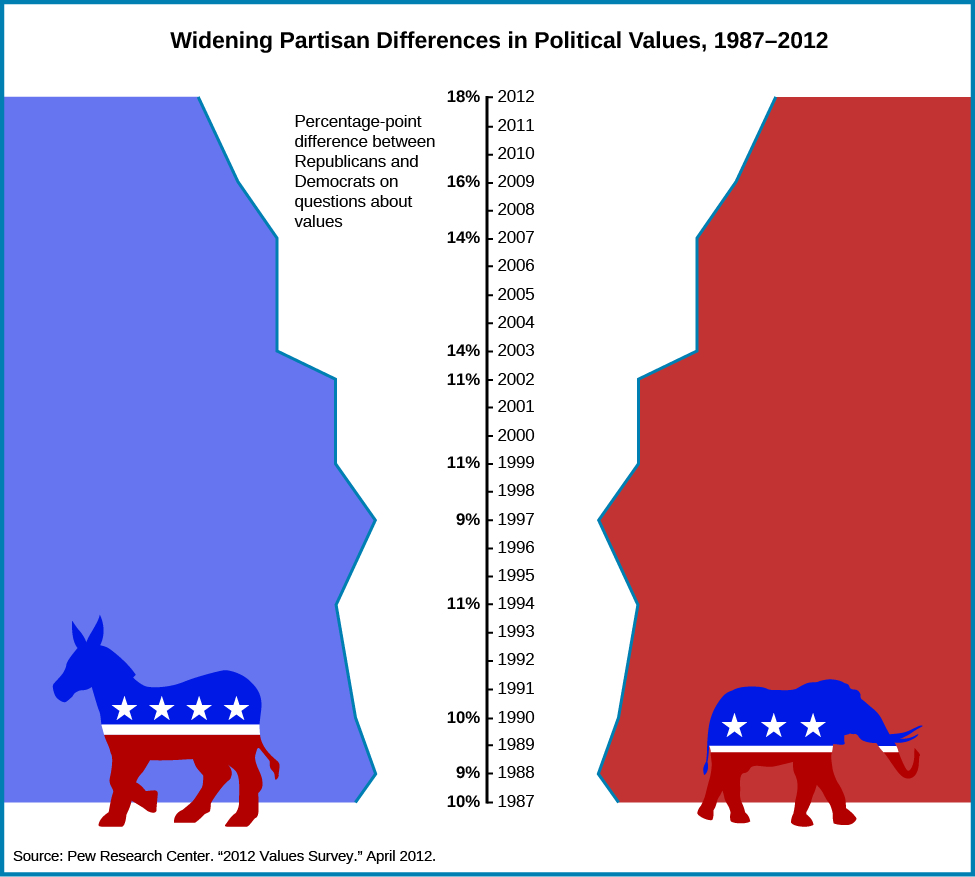
Today, polling agencies have noticed that citizens’ beliefs have become far more polarized, or widely opposed, over the last decade.Pew Research Center. 2014. “Political Polarization in the American Public.” Pew Research Center. June 12, 2014. http://www.people-press.org/2014/06/12/political-polarization-in-the-american-public/ (February 17, 2016). To track this polarization, Pew Research conducted a study of Republican and Democratic respondents over a twenty-five-year span. Every few years, Pew would poll respondents, asking them whether they agreed or disagreed with statements. These statements are referred to as “value questions” or “value statements,” because they measure what the respondent values. Examples of statements include “Government regulation of business usually does more harm than good,” “Labor unions are necessary to protect the working person,” and “Society should ensure all have equal opportunity to succeed.” After comparing such answers for twenty-five years, Pew Research found that Republican and Democratic respondents are increasingly answering these questions very differently. This is especially true for questions about the government and politics. In 1987, 58 percent of Democrats and 60 percent of Republicans agreed with the statement that the government controlled too much of our daily lives. In 2012, 47 percent of Democrats and 77 percent of Republicans agreed with the statement. This is an example of polarization, in which members of one party see government from a very different perspective than the members of the other party (Figure).Pew Research Center. 2015. “American Values Survey.” Pew Research Center. http://www.people-press.org/values-questions/ (February 17, 2016).
Political scientists noted this and other changes in beliefs following the 9/11 terrorist attacks on the United States, including an increase in the level of trust in governmentVirginia Chanley. 2002. “Trust in Government in the Aftermath of 9/11: Determinants and Consequences.” Political Psychology 23 (3): 469–483. and a new willingness to limit liberties for groups or citizens who “[did] not fit into the dominant cultural type.”Deborah Schildkraut. 2002. “The More Things Change... American Identity and Mass and Elite Responses to 9/11.” Political Psychology 23 (3): 532. According to some scholars, these shifts led partisanship to become more polarized than in previous decades, as more citizens began thinking of themselves as conservative or liberal rather than moderate.Joseph Bafumi and Robert Shapiro. 2009. “A New Partisan Voter.” The Journal of Politics 71 (1): 1–24. Some believe 9/11 caused a number of citizens to become more conservative overall, although it is hard to judge whether such a shift will be permanent.Liz Marlantes, “After 9/11, the Body Politic Tilts to Conservatism,” Christian Science Monitor, 16 January 2002.