
This QuickMath activity expands a basic expression that you enter. Gives answer and describes step-by-step how the answer was reached.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Date Added:
- 08/07/2023

This QuickMath activity expands a basic expression that you enter. Gives answer and describes step-by-step how the answer was reached.

This task has some aspects of a mathematical modeling problem (SMP 4) and it also illustrates SMP 1 (Making sense of a problem). Students are given all the relevant information on the nutritional labels, but they have to figure out how to use this information. They have to come up with the idea that they can set up two equations in two unknowns to solve the problem.

This tasks is an example of a mathematical modeling problem (SMP 4) and it also illustrates SMP 1 (Making sense of a problem). Students are only told that there are two ingredients in the pasta and they have a picture of the box. It might even be better to just show the picture of the box, or to bring in the box and ask the students to pose the question themselves.

The purpose of the task is to show students a situation where squaring both sides of an equation can result in an equation with more solutions than the original one. The reason for this is that it is possible to have two unequal numbers whose squares are equal.

In this video segment from Cyberchase, the CyberSquad learns how to read a thermometer as they try to keep their chocolate sculpture from melting.

This site from the Richland Community College provides lecuture notes from a class neatly organized and easy to read. Has some good information.

This lesson explains how the determinant is used for Cramer's Rule.
A math tutorial for many areas of math that contains over 2,500 pages of explanations and examples in algebra, trigonometry, calculus, and basic mathematics. Also has exams and ask-an-expert function.

The purpose of this task is to provide an opportunity for students to reason about equivalence of equations. The instruction to give reasons that do not depend on solving the equation is intended to focus attention on the transformation of equations as a deductive step.

The purpose of this task is to identify the structure in the two algebraic expressions by interpreting them in terms of a geometric context. Students will have likely seen this type of process before, so the principal source of challenge in this task is to encourage a multitude and variety of approaches, both in terms of the geometric argument and in terms of the algebraic manipulation.
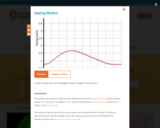
Explore your own straight-line motion using a motion sensor to generate distance versus time graphs of your own motion. Learn how changes in speed and direction affect the graph, and gain an understanding of how motion can be represented on a graph.

Students compare their own hand/foot span to Shaquille O'Neal's, then graph the data & construct a best-fit line. They can then use the information to investigate the proportionality of the human body.

This word problem is based estimating the height of a person over time. Note that there is a significant amount of rounding in the final answer. This is because people almost never report their heights more precisely than the closest half-inch. If we assume that the heights reported in the task stem are rounded to the nearest half-inch, then we should report the heights given in the solution at the same level of precision.
This web-based graphing activity explores the similarities and differences between Velocity vs. Time and Position vs. Time graphs. It interactively accepts user inputs in creating "prediction graphs", then provides real-time animations of the process being analyzed. Learners will annotate graphs to explain changes in motion, respond to question sets, and analyze why the two types of graphs appear as they do. It is appropriate for secondary physical science courses, and may also be used for remediation in preparatory high school physics courses. This item is part of the Concord Consortium, a nonprofit research and development organization dedicated to transforming education through technology. Users must register to access full functionality of all the tools available with SmartGraphs.

The typical system of equations or inequalities problem gives the system and asks for the graph of the solution. This task turns the problem around. It gives a solution set and asks for the system that corresponds to it. The purpose of this task is to give students a chance to go beyond the typical problem and make the connections between points in the coordinate plane and solutions to inequalities and equations. Students have to focus on what the graph is showing.

Students build bridges and test their strength to collect data and write an equation. The concept of slope is explored in this activity.

In this video segment from Cyberchase, Hacker and the CyberSquad race to reach the Good Vibration on staircases that grow at different rates and have steps of varying sizes.

The name linear comes from the fact that such an equation in two unknowns or variables represents a straight line. A set of such equations is called a system. This site explains all this and more.

This problem provides students with an opportunity to discover algebraic structure in a geometric context. More specifically, the student will need to divide up the given polygons into triangles and then use the fact that the sum of the angles in each triangle is 180_.

Parts (d) and (e) of this task constitute a very advanced application of the skill of making use of structure: in (d) students are being asked to use the defining property of even and odd functions to manipulate expressions involving function notation. In (e) they are asked to see the structure in the system of two equations involving functions.