
A visual representation of the Fermi Lab SENSEI experiment
- Subject:
- Physics
- Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Provider:
- Fermi National Lab
- Author:
- Fermi National Lab
- Date Added:
- 11/08/2024

A visual representation of the Fermi Lab SENSEI experiment

A visual representation of how the LUX-ZEPLIN Detector works

Student teams are challenged to evaluate the design of several liquid soaps to answer the question, “Which soap is the best?” Through two simple teacher class demonstrations and the activity investigation, students learn about surface tension and how it is measured, the properties of surfactants (soaps), and how surfactants change the surface properties of liquids. As they evaluate the engineering design of real-world products (different liquid dish washing soap brands), students see the range of design constraints such as cost, reliability, effectiveness and environmental impact. By investigating the critical micelle concentration of various soaps, students determine which requires less volume to be an effective cleaning agent, factors related to both the cost and environmental impact of the surfactant. By investigating the minimum surface tension of the soap, students determine which dissolves dirt and oil most effectively and thus cleans with the least effort. Students evaluate these competing criteria and make their own determination as to which of five liquid soaps make the “best” soap, giving their own evidence and scientific reasoning. They make the connection between gathered data and the real-world experience in using these liquid soaps.

A visual representation of the Dark SRF experiment at Fermi lab
Students apply everything they have learned about light properties and laser technologies to designing, constructing and presenting laser-based security systems that protect the school's mummified troll. In the associated activity, students "test their mettle" by constructing their security system using a PVC pipe frame, lasers and mirrors. In the lesson, students "go public" by creating informational presentations that explain their systems, and serve as embedded assessment, testing each student's understanding of light properties.
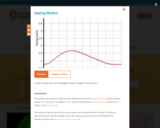
Explore your own straight-line motion using a motion sensor to generate distance versus time graphs of your own motion. Learn how changes in speed and direction affect the graph, and gain an understanding of how motion can be represented on a graph.
This article describes the basics of thermography or thermal imaging, and how this technique can inspire a data collection activity to teach about heat transfer and energy efficiency.
Students learn about STEM education through an engineering design challenge that focuses on improving building materials used in shantytowns. First, they consider the factors that lead to shantytown development. After researching the implications of living in shantytowns, students design, build and test cement-based concrete block composites made of discarded and/or recycled materials. The aim is to make a material that is resistant to degradation by chemicals or climate, can withstand natural disasters, and endure through human-made conditions (such as urban overcrowding or pollution). The composites must be made of materials that are inexpensive and readily available so that they are viable alternative in shantytown communities. Students assess the results both chemically and physically and then iterate their designs with the materials that proved to be strongest.
Students explore the basic physics behind walking, and the design and engineering of shoes to accommodate different gaits. They are introduced to pressure, force and impulse as they relate to shoes, walking and running. Students learn about the mechanics of walking, shoe design and common gait misalignments that often lead to injury.
This activity is an investigation of free fall and projectile motion through a track and field situation.
Students use their understanding of projectile physics and fluid dynamics to find the water pressure in water guns. By measuring the range of the water jets, they are able to calculate the theoretical pressure. Students create graphs to analyze how the predicted pressure relates to the number of times they pump the water gun before shooting.

In this adapted ZOOM video segment, cast members calculate how much water they each use during a typical shower. They compare their results to their original predictions.
Student teams make polymers using ordinary household supplies (glue, borax, water). They experiment with the semi-solid material when warm and cold to see and feel its elastic and viscous properties. Students will begin to understand how the electrical forces between particles change as temperature or the force applied to the substance changes. Is it a solid, a liquid, or something in between? How might it be used?
In this activity, students play the game Simon Says to make the amplitudes and wavelengths defined by the teacher. First they play alone, and then they play with a partner using a piece of rope.
Students build and use a very basic Coulter electric sensing zone particle counter to count an unknown number of particles in a sample of "paint" to determine if enough particles per ml of "paint" exist to meet a quality standard. In a lab experiment, student teams each build an apparatus and circuit, set up data acquisition equipment, make a salt-soap solution, test liquid flow in the apparatus, take data, and make graphs to count particles.

This pathway explores the concept of simple harmonic motion. The pendulum and spring are used as foundational examples that are used to develop more complex models. Advanced application such as resonsnce are discussed

This video segment from IdahoPTV's D4K lists, describes and shows examples of the 6 simple machines and how they make work easier.

Through a five-lesson series with five activities, students are introduced to six simple machines inclined plane, wedge, screw, lever, pulley, wheel-and-axle as well as compound machines, which are combinations of two or more simple machines. Once students understand about work (work = force x distance), they become familiar with the machines' mechanical advantages, and see how they make work easier. Through an introduction to compound machines, students begin to think critically about machine inventions and their pervasive roles in our lives. After learning about Rube Goldberg contraptions absurd inventions that complete simple tasks in complicated ways they evaluate the importance and usefulness of the many machines around them. Through the hands-on activities, students draw designs for contraptions that could move a circus elephant into a rail car, create a construction site ramp design by measuring different inclined planes and calculating the ideal vs. actual mechanical advantage of each, compare the theoretical and actual mechanical advantages of different pulley systems conceived to save a whale, build and test grape catapults made with popsicle sticks and rubber bands, and follow the steps of the engineering design process to design and build Rube Goldberg machines.
Students apply the mechanical advantages and problem-solving capabilities of six types of simple machines (wedge, wheel and axle, lever, inclined plane, screw, pulley) as they discuss modern structures in the spirit of the engineers and builders of the great pyramids. While learning the steps of the engineering design process, students practice teamwork, creativity and problem solving.

Students research simple machines and other mechanisms as they learn about and make Rube Goldberg machines. Working in teams, students design and build their own Rube Goldberg devices with 10 separate steps, including at least six simple machines. In addition to the use of readily available classroom craft supplies, 3D printers may be used (if available) to design and print one or more device mechanisms. Students love this open-ended, team-building project with great potential for creativity and humor.