
A "one star" geometry problem that requires finding the visual pattern and applying and pattern extensions to solve the false ceiling problem.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Lesson Plan
- Provider:
- MathsChallenge.net
- Date Added:
- 12/01/2023

A "one star" geometry problem that requires finding the visual pattern and applying and pattern extensions to solve the false ceiling problem.

A "one star" geometry problem that requires visualizing to find how many different patterns can be made.

A "one star" geometry problem that requires finding the visual pattern and applying logic with basic math skills to find the perimeter from the sequence.
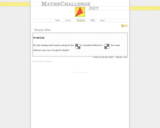
A "one star" geometry problem that requires finding the visual pattern and applying logic with basic math skills to find the patterns.
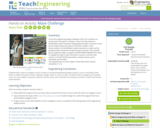
As the first engineering design challenge of the unit, students are introduced to the logic for solving a maze. First they observe a blindfolded student volunteer being guided through a classroom maze by the simple verbal instructions of another student. In this demonstration, the blindfolded student represents a robot and the guiding student represents programming commands. Then student groups apply that logic to program LEGO MINDSTORMS(TM) NXT robots to navigate through a maze, first with no sensors, and then with sensors. A PowerPoint® presentation, pre/post quizzes and a worksheet are provided.

Sharpen your logical thinking and see if you can figure out the strategy to get to the target number before the computer.

Excellent interactive challenge working with cube nets to stack them in a specific order. Manipulate the cubes online to solve the problem.

In this enrichment game, the nets for nine solids are displayed. The twist is that each net has been cut into two pieces. The challenge is find the pieces that go together.

Using your reasoning skills and the clues provided, try to figure out who is sitting where at this table of six. Check the solution and see if you are correct. You can choose similar games and math problems on this page, or choose math exercises at a higher or lower level from the left navigation bar. Lots of math fun brought to you by the Millennium Mathematics Project from the University of Cambridge.
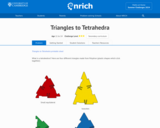
Given an unlimited number of a specific type of equilateral, isosceles, and right triangles create as many tetrahedra as are possible. Includes printout.

NZMaths is a New Zealand teacher resource that provides lesson plans for students in algebra, geometry, measurement, numbers, statistics, logic and reasoning.
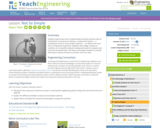
Students expand upon their understanding of simple machines with an introduction to compound machines. A compound machine a combination of two or more simple machines can affect work more than its individual components. Engineers who design compound machines aim to benefit society by lessening the amount of work that people exert for even common household tasks. This lesson encourages students to critically think about machine inventions and their role in our lives.

Find the area of several figures to prove the Pythagorean theorem. Complete quiz to check understanding. [5:16]

A simple discussion of the differences between inductive and deductive reasoning. Helpful to anyone who is having difficulty differentiating between the two.

Play a game of concentration by matching terms used in the scientific method to their proper description.

This site provides a good explanation of deductive and inductive thinking.
Students learn how two LEGO MINDSTORMS(TM) NXT intelligent bricks can be programmed so that one can remotely control the other. They learn about the components and functionality in the (provided) controller and receiver programs. When its buttons are pressed, the NXT brick assigned as the remote control device uses the controller program to send Bluetooth® messages. When the NXT taskbot/brick assigned as the receiver receives certain Bluetooth messages, it moves, as specified by the receiver program. Students examine how the programs and devices work in tandem, gaining skills as they play "robot soccer." As the concluding activity in this unit, this activity provides a deeper dimension of understanding programming logic compared to previous activities in this unit and introduces the relatively new and growing concept of wireless communication. A PowerPoint® presentation, pre/post quizzes and a worksheet are provided.

Do you know how to get to Sesame Street? This collection is designed to engage preschoolers in everyday learning by teaching core skills in Math, Literacy, STEM, and Social and Emotional Development. Here you'll find hundreds of videos, games, and printable materials to help you to excite even the youngest learners.

In this video, meet Rio, a captive California sea lion who has helped research biologists to better understand the cognitive abilities of this species. See how Rio has learned that certain sounds are associated with certain letters or numbers, and observe how she demonstrates the higher order reasoning skill of logic. Biologist Colleen Reichmuth explains how Rio has learned that all letters can be grouped together and is able to use a logic rule to solve a new problem. Consider how this reasoning ability is related to language. [4:42]

Students learn basic concepts of robotic logic and programming by working with Boe-Bot robotsâa simple programmable robotic platform designed to illustrate basic robotic concepts. Under the guidance of the instructor and a provided lab manual, student groups build simple circuits and write codes to make their robots perform a variety of tasks, including obstacle and light detection, line following and other motion routines. Eight sub-activities focus on different sensors, including physical sensors, phototransistors and infrared headlights. Students test their newly acquired skills in the final activity, in which they program their robots to navigate an obstacle course.