
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Define observational learning
Discuss the steps in the modeling process
Explain the prosocial and antisocial effects of observational learning
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 09/20/2018

By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Define observational learning
Discuss the steps in the modeling process
Explain the prosocial and antisocial effects of observational learning

Working individually or in pairs, students compete to design, create, test and redesign free-standing, weight-bearing towers using Kapla(TM) wooden blocks. The challenge is to build the tallest tower while meeting the design criteria and minimizing the amount of material used all within a time limit. Students experiment with different geometric shapes used in structural designs and determine how design choices affect the height and strength of structures, becoming comfortable with the concepts of structural members and modeling.
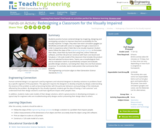
Students practice human-centered design by imagining, designing and prototyping a product to improve classroom accessibility for the visually impaired. To begin, they wear low-vision simulation goggles (or blindfolds) and walk with canes to navigate through a classroom in order to experience what it feels like to be visually impaired. Student teams follow the steps of the engineering design process to formulate their ideas, draw them by hand and using free, online Tinkercad software, and then 3D-print (or construct with foam core board and hot glue) a 1:20-scale model of the classroom that includes the product idea and selected furniture items. Teams use a morphological chart and an evaluation matrix to quantitatively compare and evaluate possible design solutions, narrowing their ideas into one final solution to pursue. To conclude, teams make posters that summarize their projects.
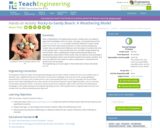
Given a hypothetical civil engineering scenario, student pairs are tasked to apply their knowledge of the rock cycle, rock types, rock weathering and the engineering design process to model a potential method to create a sandy beach from three rocky island shorelines. For their abrasion weathering models, they use wide-mouth lidded jars and three types of candies that serve as the testing “rocks.” They simulate both low- and high-energy weathering environments. After completing the simple weathering techniques and analyzing their observations of the results, they conclude by recommending to the island developer which rocky shoreline would be the easiest, simplest, and most cost-effective from which to create a sandy beach. A worksheet and pre/post quiz are provided.
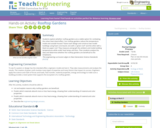
Students explore whether rooftop gardens are a viable option for combating the urban heat island effect. Can rooftop gardens reduce the temperature inside and outside houses? Teams each design and construct two model buildings using foam core board, one with a "green roof" and the other with a black tar paper roof. They measure and graph the ambient and inside building temperatures while under heat lamps and fans. Then students analyze the data and determine whether the rooftop gardens are beneficial to the inhabitants.

Sam Gilliam is profiled at this site in a format that begins with a lengthy biographical sketch of his life. His works are then listed by appearance in the museum's database. Each work is presented in thumbnail format with brief information including title of work and date of creation.
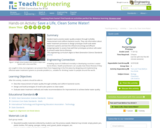
Student teams practice water quality analysis through turbidity measurement and coliform bacteria counts. They use information about water treatment processes to design prototype small-scale water treatment systems and test the influent (incoming) and effluent (outgoing) water to assess how well their prototypes produce safe water to prevent water-borne illnesses.
Students learn that engineers develop different polymers to serve various functions and are introduced to selectively permeable membranes. In a warm-up activity, they construct models of selectively permeable membranes using common household materials, and are reminded about simple diffusion and passive transport. In the main activity, student pairs test and compare the selective permeability of everyday polymer materials engineered for food storage (including plastic grocery bags, zipper sandwich bags, and plastic wrap) with various in-solution molecules (iodine, corn starch, food coloring, marker dye), assess how the polymer’s permeability relates to its function/purpose, and compare that to the permeability of dialysis tubing (which simulates a cell membrane).

Students are introduced to the concepts of graywater and water reuse within households. They calculate the amount of used water a family generates in one day and use a model of home plumbing to find out how much graywater is produced in homes every day. They graph their results and discuss energy efficiency implications. Students are then challenged to find ways to reduce water use within the home.

Students learn about how engineers design and build shake tables to test the ability of buildings to withstand the various types of seismic waves generated by earthquakes. Just like engineers, students design and build shake tables to test their own model buildings made of toothpicks and mini marshmallows. Once students are satisfied with the performance of their buildings, they put them through a one-minute simulated earthquake challenge.
Students investigate the critical nature of foundations as they learn differences between shallow and deep foundations, including the concepts of bearing pressure and settlement. Using models representing a shallow foundation and a deep pile foundation, they test, see and feel the effects in a cardboard box test bed composed of layers of pebbles, soil and sand. They also make bearing pressure calculations and recommendations for which type of foundations to use in various engineering scenarios.
Students learn how engineering design is applied to solve healthcare problems by using an engineering tool called simulation. While engineering design is commonly used to study and design everything from bridges, factories, airports to space shuttles, the use of engineering design to study healthcare administration and delivery is a relatively new concept.
Students are introduced to the engineering challenges involved with interplanetary space travel. In particular, they learn about the gravity assist or "slingshot" maneuver often used by engineers to send spacecraft to the outer planets. Using magnets and ball bearings to simulate a planetary flyby, students investigate what factors influence the deflection angle of a gravity assist maneuver.
Students learn why shock absorbers are necessary on vehicles, how they dampen the action of springs, and what factors determine the amount of dampening. They conduct an experiment to determine the effect of spring strength and port diameter on the effectiveness of a shock absorber. Using a syringe, a set of springs, and liquids of different viscosities, students determine the effects of changing pressures and liquids on the action of a model shock absorber. They analyze their data through the lens of an engineer.
To experience the three types of material stress related to rocks â tensional, compressional and shear â students break bars of soap using only their hands. They apply force created by the muscles in their own hands to put pressure on the soap, a model for the larger scale, real-world phenomena that forms, shapes and moves the rocks of our planet. They also learn the real-life implications of understanding stress in rocks, both for predicting natural hazards and building safe structures.
Students learn about one method used in environmental site assessments. They practice soil sampling by creating soil cores, studying soil profiles and characterizing soil profiles in borehole logs. They use their analysis to make predictions about what is going on in the soil and what it might mean to an engineer developing the area.

Working as if they were engineers, students design and construct model solar sails made of aluminum foil to move cardboard tube satellites through “space” on a string. Working in teams, they follow the engineering design thinking steps—empathize, define, ideate, prototype, test, redesign—to design and test small-scale solar sails for satellites and space probes. During the process, learn about Newton’s laws of motion and the transfer of energy from wave energy to mechanical energy. A student activity worksheet is provided.

To understand the challenges of satellite construction, student teams design and create model spacecraft to protect vital components from the harsh conditions found on Mercury and Venus. They use slices of butter in plastic eggs to represent the internal data collection components of the spacecraft. To discover the strengths and weaknesses of their designs, they test their unique thermal protection systems in a planet simulation test box that provides higher temperature and pressure conditions.

As if they are engineers, students are tasked to design solar-powered model vehicles that are speedy and compact in order to make recommendations to a local car sales company. Teams familiarize themselves with the materials by building solar-panel model car prototypes, following kit instructions, which they test for speed. After making design improvements, they test again. Then they take measurements and calculate the volume of each team’s vehicle. They rank all teams’ vehicles by speed and by size. After data analyses, reflection and team discussion, students write recommendations to the car company about the vehicle they think is best for consumers. Youngsters experience key portions of the engineering design process and learn the importance of testing and collaborating in order to make better products. Pre/post-quizzes and numerous worksheets and handouts are provided.

Watch Spinner the Spider draw the letters of the alphabet, both upper and lower case.