
Explore material properties as Ruff Ruffman tries to find the right material to transform Fluff the Rhino into Fluff the Dog. [4:08]
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Science
- Material Type:
- Audio/Video
- Provider:
- PBS LearningMedia
- Date Added:
- 11/06/2023

Explore material properties as Ruff Ruffman tries to find the right material to transform Fluff the Rhino into Fluff the Dog. [4:08]
Explore sports science and build a ramp that will roll a ball right to the target.

Learn about wearable science and material properties alongside Ruff Ruffman.

Help Fluff the Rhino dress for a trip in this activity from The Ruff Ruffman Show. Fluff will need different clothing.
Explore sports science as Ruff Ruffman tries to win his plushie back by defeating Glen's Milk Bottle Pyramid of Doom. [5:49]

Explore structural science as Ruff Ruffman uses his new service, called "Ask Ruff First" or "ARF, to build a topple-proof birdbath. [4:45]

Astronomer Carl Sagan discusses the possibility of time travel in this audio-enhanced interview from the NOVAWeb site.
Science Over Everything is a blog dedicated to helping middle and high school students understand current events in science and why they are relevant to their daily lives. Our site is intended to be a resource for teachers, providing each blog post with classroom activities to help the students comprehend what they are reading and fit the articles in a school's curriculum.
Students learn about STEM education through an engineering design challenge that focuses on improving building materials used in shantytowns. First, they consider the factors that lead to shantytown development. After researching the implications of living in shantytowns, students design, build and test cement-based concrete block composites made of discarded and/or recycled materials. The aim is to make a material that is resistant to degradation by chemicals or climate, can withstand natural disasters, and endure through human-made conditions (such as urban overcrowding or pollution). The composites must be made of materials that are inexpensive and readily available so that they are viable alternative in shantytown communities. Students assess the results both chemically and physically and then iterate their designs with the materials that proved to be strongest.

This video segment from IdahoPTV's D4K lists, describes and shows examples of the 6 simple machines and how they make work easier.

In this video segment adapted from NOVA scienceNOW, learn about engineering innovations that could help detect a bridge's structural weaknesses before they become dangerous.

This video segment adapted from NOVA/FRONTLINE looks at American energy consumption and the resulting production of greenhouse gases.

In this video from DragonflyTV, follow the investigation of Isaac and Anjali as they record, measure, and analyze data about how the Sun's position in the sky affects a solar-powered car's speed.
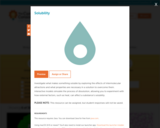
Investigate what makes something soluble by exploring the effects of intermolecular attractions and what properties are necessary in a solution to overcome them. Interactive models simulate the process of dissolution, allowing you to experiment with how external factors, such as heat, can affect a substance's solubility.
This lesson is designed to help students understand that vibrations are responsible for the sounds we hear. Additionally, they learn that sound vibrations can travel through different mediums. Students experience vibrations using several of their senses: They feel the vibrations in their throat as they hum music, and on their lips as they play their straw kazoos. They see that when a ruler is struck, it vibrates, producing a sound. Drums are also used to show vibrations, as students watch grains of rice bouncing on the surface of the drum after it has been hit, and a laser pointer creates a laser show in the classroom when reflected off a vibrating mirror. Finally, students design a test that uses their sense of hearing to judge the effectiveness of different solids to transmit sound vibrations.

This interactive quiz from the NOVA Web site features an array of interesting facts about the nature of sound underwater.

This video segment, adapted from ZOOM, explores how sound waves travel differently through solids than through air, in this case, a metal clothes hanger.
The students are to calculate the specific heat of three metal objects. Then they are to determine the type of metal.

This video segment adapted from Shedding Light on Science uses historical illustrations and everyday examples to show that light has a speed and does not travel instantaneously.

This video segment from IdahoPTV's D4K explains and gives examples of the 4 states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma.